Smart Heating Solutions
How to Choose the Right Electric Heater for Your House: A Comprehensive Guide
As the demand for efficient heating solutions continues to rise, selecting the right electric heater for house use has become paramount for homeowners. With the U.S. Department of Energy reporting that heating accounts for nearly 30% of residential energy consumption, making the right choice can significantly impact energy bills and comfort levels. According to a recent study by the Energy Information Administration, electric heating options are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience, ease of installation, and the rapid advancement of technology in the sector.
Expert Robert Kingston, a renowned heating consultant, emphasizes this point by stating, “Choosing the appropriate electric heater for house use is not just about warming your space; it’s about optimizing energy efficiency and safety for your family.” With various models available, from baseboard heaters to portable units, understanding the specific needs of your home is crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential factors to consider when selecting an electric heater for house use, arming you with the knowledge to make an informed decision that aligns with your heating requirements.

How Electric Heaters Work: Understanding Different Types and Technologies
Electric heaters operate through various technologies, each suited for different heating needs and preferences. The most common types include resistance heaters, which convert electrical energy directly into heat, typically using metal coils that glow red-hot. This method is straightforward and effective for quickly warming small spaces.
Another prevalent technology is convection heating, which relies on the natural circulation of air. Convection heaters warm the surrounding air, causing it to rise and circulate, thereby distributing heat more evenly throughout the room. This type tends to be favored for larger areas due to its efficient heat distribution.
In addition to resistance and convection heating, there are also radiant heaters that focus on heating objects and people directly rather than the air. These heaters utilize infrared technology, producing heat through infrared radiation, similar to the warmth from the sun.
Radiant heaters are particularly effective in outdoor settings or in spaces with high ceilings, where conventional methods may struggle to maintain warmth. Each of these technologies has distinct characteristics that resonate differently depending on the environment, making it crucial to understand their mechanics when selecting an electric heater for a specific space.
Assessment of Heating Needs: Calculating BTUs for Your Space
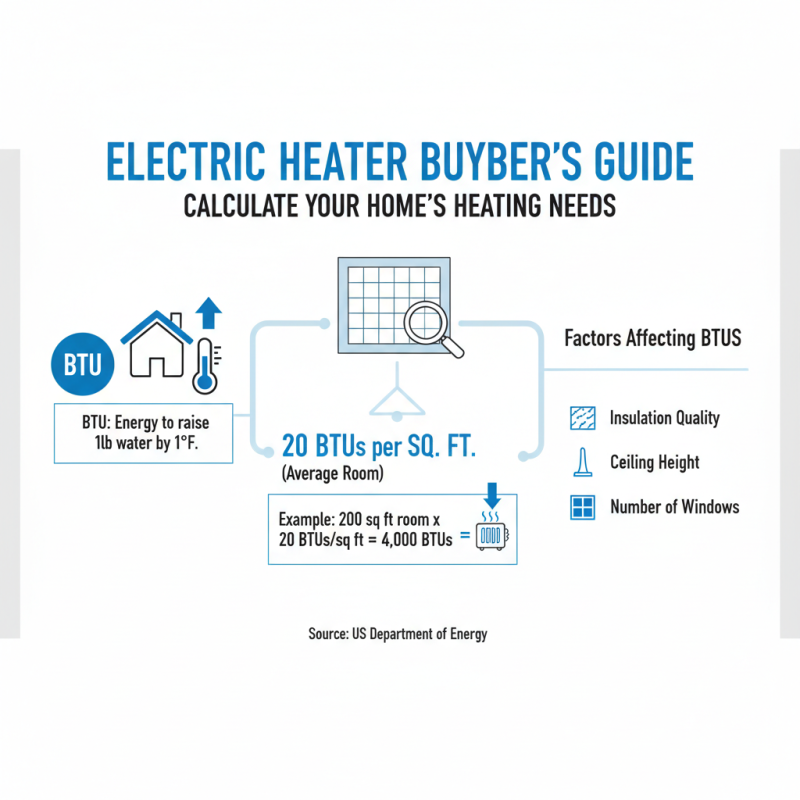
When choosing the right electric heater for your home, it’s essential to assess your heating needs accurately. A crucial factor in this assessment is calculating the required British Thermal Units (BTUs) for your space. BTUs represent the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the average room typically requires about 20 BTUs per square foot. For example, a 200-square-foot room would necessitate around 4,000 BTUs for adequate heating. These figures can vary based on factors such as insulation quality, ceiling height, and the number of windows present.
When calculating your home’s BTU requirements, consider consulting with online calculators or energy audits that can provide more tailored estimates. Remember to account for the insulation levels and local climate conditions, as temperate regions require lower BTUs compared to colder areas. It is wise to overestimate slightly to ensure comfort during extreme weather conditions.
Tips: Always factor in additional BTUs for spaces with high ceilings or numerous windows, as these elements can lead to increased heat loss. Additionally, consider zoned heating for larger homes to enhance efficiency and comfort. Finally, regular maintenance of your heating system can help maintain efficiency, ensuring you meet your heating needs effectively.
Energy Efficiency Ratings: Comparing Electric Heater Options
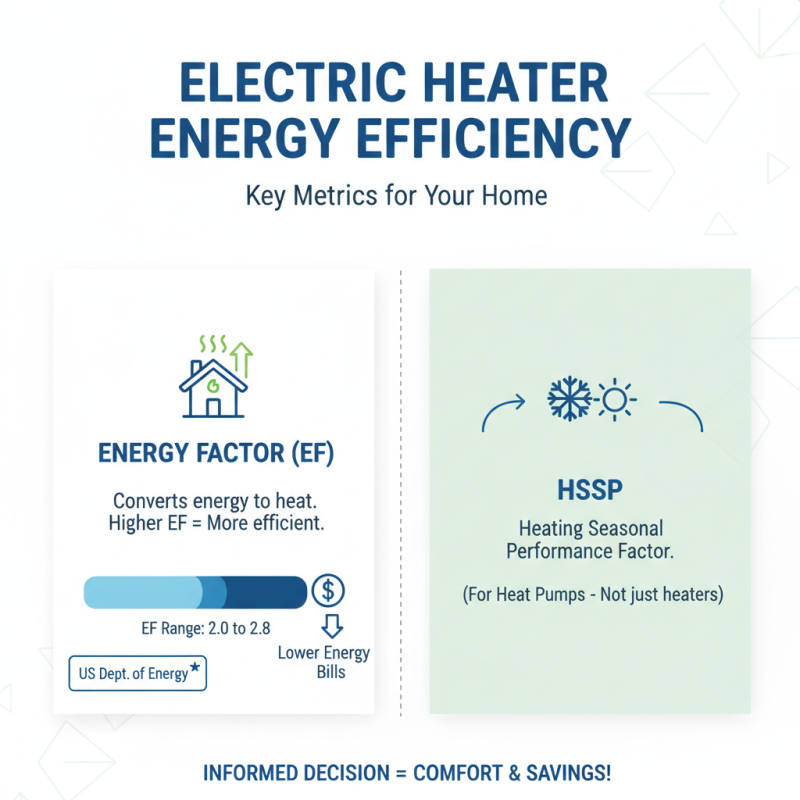
When selecting an electric heater for your home, understanding energy efficiency ratings is crucial for making an informed decision. The most common metrics used to evaluate these heaters include the Energy Factor (EF) and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF). According to the U.S. Department of Energy, a higher EF indicates a more efficient heater that converts energy into heat effectively, ultimately leading to lower energy bills. In general, electric heaters typically have an EF ranging from 2.0 to 2.8, with models on the higher end of this scale being significantly more energy-efficient.
Moreover, examining the HSPF provides insight into a heater's efficiency over an entire heating season. This rating assesses the total heat output during the season divided by the total energy consumed. For electric heat pumps, a good HSPF rating is above 8.0, indicating a competent performance in energy conservation over time. Industry data suggests that investing in heaters with superior energy efficiency ratings can lead to savings of up to 30% in energy costs annually, making a long-term financial impact that should not be overlooked when making your selection.
Safety Features in Electric Heaters: What to Look For
When selecting an electric heater for your home, safety features should be a primary concern. According to a report by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), heating equipment is involved in nearly 50,000 residential fires annually in the U.S., emphasizing the need for robust safety mechanisms.
Essential safety features to consider include overheat protection, which automatically shuts off the unit if it reaches an unsafe temperature, and tip-over protection, which cuts power if the heater is accidentally knocked over. These features are crucial in preventing dangerous situations, particularly in homes with children and pets.
Additionally, it's important to look for models that come with a safety certification from recognized bodies such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) or the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). These certifications indicate that the heater has undergone rigorous testing to meet safety standards.
A study by the Department of Energy highlights that heaters which incorporate safety features not only reduce the risk of fires but also promote more efficient energy use, leading to lower utility bills. By prioritizing safety when choosing an electric heater, homeowners can ensure a warm and secure living environment while minimizing risks associated with heating equipment.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Energy Savings
When choosing an electric heater, it's essential to conduct a thorough cost analysis that compares your initial investment against potential long-term energy savings. The upfront cost of electric heaters can vary significantly depending on their size, type, and features. For instance, while a more expensive model might require a higher initial expenditure, it may also include advanced features such as programmable thermostats or energy-efficient settings that can lead to reduced consumption over time.
In contrast, a lower-cost heater may seem appealing; however, it might have higher operational costs due to lower efficiency. Understanding your home's heating needs and the specific characteristics of different heaters can help you predict future energy expenditures. It’s also worth considering the product's lifespan and potential maintenance costs. By calculating estimated energy savings over several years, you can achieve a clearer picture of the total cost of ownership, allowing you to make a more informed decision that benefits both your wallet and comfort.
How to Choose the Right Electric Heater for Your House: A Comprehensive Guide - Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Energy Savings
| Heater Type | Initial Investment ($) | Average Annual Operating Cost ($) | Energy Efficiency Rating | Expected Lifespan (years) | Total Cost Over 10 Years ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convection Heater | 300 | 250 | 80% | 15 | 2,800 |
| Radiant Heater | 400 | 200 | 85% | 20 | 2,500 |
| Infrared Heater | 500 | 180 | 90% | 25 | 2,200 |
| Fan Heater | 200 | 300 | 75% | 10 | 3,000 |
| Oil-Filled Heater | 350 | 230 | 80% | 20 | 2,900 |
Related Posts
-
Why You Need a Workshop Heater for Winter: Benefits and Tips
-

Top 2025 Line Voltage Thermostat Features You Need to Know
-

Top 10 Wall Mounted Heaters for Efficient Home Heating Solutions
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Baseboard Heater Thermostat
-

Top 10 Wall Mounted Heaters for Efficient Home Heating in 2023
-

Best Wall Heater Options for Efficient Heating in Every Home